Blog Post
SQL Server - Display Indexes With Their Columns & Included Columns
Display SQL Server Index Details – Type, Key Columns, Included Columns
Have you ever wanted a query that would give you a list of all the indexes that exist in your database along with details of the index type and all the columns that are a part of the index key and all included columns?
Well have a look at this query. It might help:
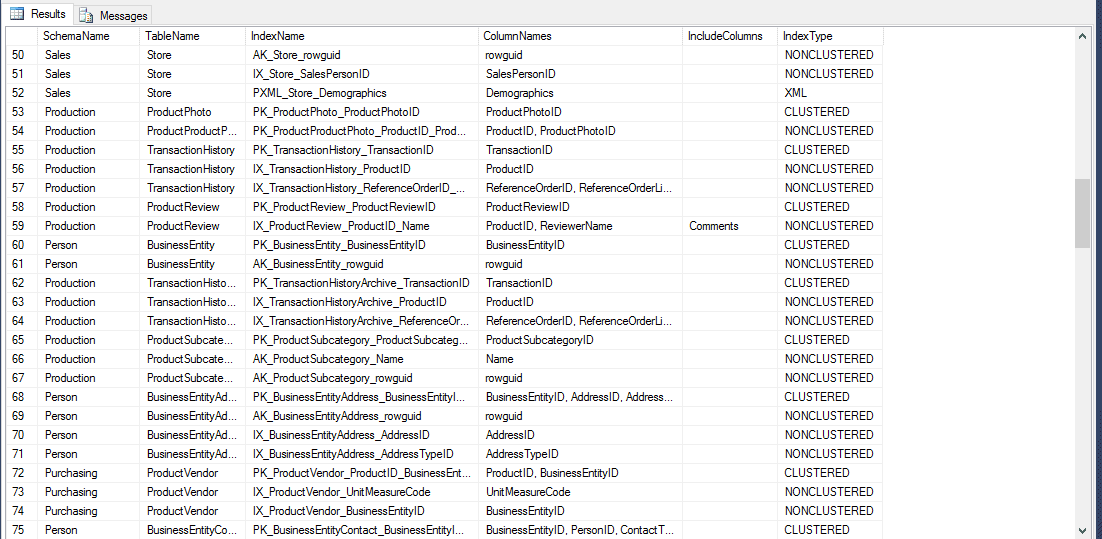
The following screen shot shows some sample output when this query is run against the AdventureWorks2014 sample database:
We can see that there is an index called [IX_ProductReview_ProductID_Name] on the table called [Production].[ProductReview]. The query output shows that this is a non clustered composite index based on the ProductID and ReviewerName columns and with an included column called Comments.
Here is the CREATE INDEX script generated from this index:
If you would like to learn more about SQL Server indexing why not take a look at our SQL Server Performance & Tuning training course. It covers plenty of interesting things about indexing:
Indexing: OLTP, OLAP, Hybrid
Index Optimisation
Indexing: UNIQUE Index, DUPLICATE Index, NONCLUSTERED Index, CLUSTERED Index, Covering Index, Composite Index, INCLUDE Index, Filtered Indexes
Creating Indexes
Index Structure: B-Tree Index, Non-clustered B-Tree, Clustered B-Tree
Non-Clustered Index on a Table Containing Clustered Index
The sys.indexes View
When To Index
The Query Optimizer
Index Tuning
A Few Tips: Don’t Over Index, Composite Indexes, Large Data Types, Be Selective, Optimize, Clustered Indexes, Targets For Index Tuning
Growing Indexes
FILLFACTOR: Choosing the FILLFACTOR, PADINDEX
The Database Engine Tuning Advisor: Using A Workload File, Using A Selected Query In Query Analyzer, Saving An Index Tuning Wizard Script, Accepting Recommendations
Monitoring Index Usage
Table Hints
Indexed Views
Displaying Information About Indexes: Viewing Index Records, Viewing Pages
Index Depth & Density: DBCC SHOWCONTIG, sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats Function
Defragmenting/Rebuilding An Index
Online Index Building
Index Usage
Dynamic Management Views & Functions for Indexes: sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats, sys.dm_db_index_operational_stats, sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats
Share This Post
Mandy Doward
Managing Director
PTR’s owner and Managing Director is a Microsoft certified Business Intelligence (BI) Consultant, with over 35 years of experience working with data analytics and BI.
Frequently Asked Questions
Couldn’t find the answer you were looking for? Feel free to reach out to us! Our team of experts is here to help.
Contact Us


